What Are the Health Benefits of Monounsaturated Fats

You help your body when you choose foods rich in monounsaturated fats. These healthy fats support your heart, lower bad cholesterol, and may improve blood sugar control. Monounsaturated fats come mostly from plant oils, such as olive and canola oil. They have one double bond in their structure, which sets them apart from saturated and trans fats that can harm your health. Experts recommend that unsaturated fats, including monounsaturated fats, make up 20-35% of your daily calories. The benefits of monounsaturated fats make them a smart choice for your well-being.
Key Takeaways
Monounsaturated fats support heart health by lowering bad cholesterol and reducing blood pressure.
Eating foods rich in monounsaturated fats, like olive oil, avocados, and nuts, helps improve blood sugar control and reduce inflammation.
Replacing saturated and trans fats with monounsaturated fats can lower the risk of heart disease and aid weight management.
Use plant-based oils such as olive or avocado oil for cooking and add nuts or avocado to meals for a healthy fat boost.
Experts recommend that 15% to 20% of your daily calories come from monounsaturated fats for better overall health.
What Are Monounsaturated Fats?
Definition
Monounsaturated fats are a type of dietary fat that you find mostly in plant-based foods and oils. These fats have a unique chemical structure. Each molecule contains one double bond in its fatty acid chain. This double bond is usually in the cis configuration, which gives the molecule a bent shape. Because of this bend, monounsaturated fats stay liquid at room temperature. You can spot them in foods like olive oil, avocados, and nuts.
Your body needs fat for many reasons. Fat provides energy, helps build cell membranes, and supports brain function. It also helps you absorb vitamins such as A, D, E, and K. Some people think fat is bad for you, but your body cannot work well without it. Monounsaturated fats supply essential fatty acids that your body cannot make on its own. They also play a role in hormone regulation and immune function.
Tip: Choose foods with monounsaturated fats to support your health and keep your meals tasty.
Comparison to Other Fats
You may wonder how monounsaturated fats differ from other fats. Here is a simple breakdown:
Type of Fat | Structure | Common Sources | Health Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
Monounsaturated | One cis double bond (bent chain) | Olive oil, avocados, nuts, seeds | Supports heart health |
Saturated | No double bonds (straight chain) | Butter, lard, fatty meats, dairy | Raises LDL cholesterol |
Trans | One or more trans double bonds | Processed snacks, fried foods | Increases heart disease risk |
Saturated fats have no double bonds. Their straight chains make them solid at room temperature. You find them in animal products like butter and fatty meats. Eating too much saturated fat can raise your LDL cholesterol, which is bad for your heart.
Trans fats are unsaturated but have trans double bonds. This makes their chains straight, like saturated fats. Trans fats come from processed foods and hydrogenated oils. They are harmful and increase your risk of heart disease.
Monounsaturated fats stand out because they help lower harmful LDL cholesterol and may improve your cholesterol profile. National dietary guidelines suggest you replace saturated and trans fats with monounsaturated fats for better heart health.
Note: The Mediterranean diet, rich in monounsaturated fats, has shown lower rates of heart disease in many studies.
Benefits of Monounsaturated Fats
Heart Health
You can protect your heart by choosing foods high in monounsaturated fats. Many studies show that these fats help lower your risk of heart disease. Diets rich in monounsaturated fats improve important heart health markers, such as blood pressure and cholesterol. The famous Lyon Diet Heart Study found that people who ate more monounsaturated fats after a heart attack had better outcomes. The American Heart Association recommends replacing saturated and trans fats with monounsaturated fats to support your heart. When you eat more of these healthy fats, you help your body lower bad cholesterol and raise good cholesterol. The Mediterranean diet, which is high in monounsaturated fats, is linked to fewer heart attacks and strokes.
Monounsaturated fats work in several ways to keep your heart healthy. They lower LDL cholesterol, reduce inflammation, and protect your blood vessels. These fats also help your body make larger, less harmful LDL particles. By improving your cholesterol profile and reducing blood pressure, monounsaturated fats lower your risk of heart disease.
Tip: Try using olive oil or avocado oil in your cooking to boost your heart health.
Cholesterol Levels
Monounsaturated fats play a key role in managing cholesterol. They help raise HDL (good) cholesterol and lower LDL (bad) cholesterol. This balance is important for keeping your arteries clear and reducing your risk of heart problems.
Parameter | Effect of High Monounsaturated Fat Diet vs Low MUFA Diet | Statistical Significance (p-value) |
|---|---|---|
HDL cholesterol increase | 12.5% greater increase (0.12 mmol/L) | 0.003 |
Apolipoprotein AI increase | 10.1% greater increase (0.12 mmol/L) | 0.001 |
LDL cholesterol reduction | No significant difference between diets | 0.43 |
Ratio of total to HDL cholesterol | 6.5% greater reduction | Not specified |
Apolipoprotein B to AI ratio | 5.1% greater reduction | Not specified |
High-sensitivity C-reactive protein | 76.4% greater reduction | Not specified |
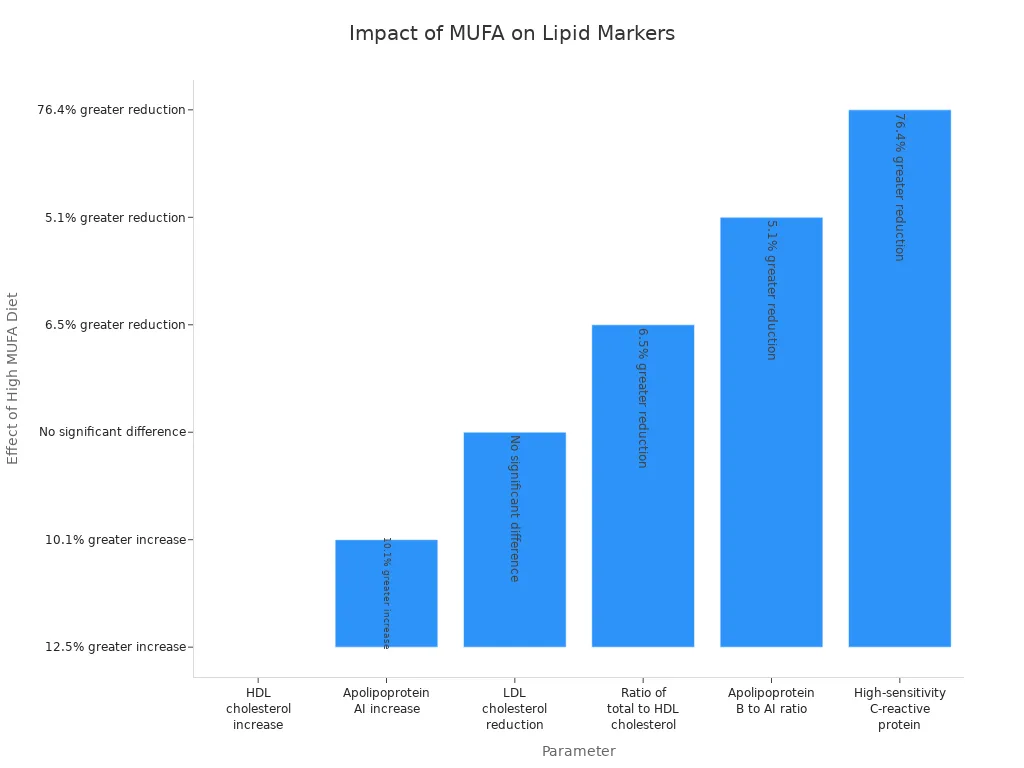
You can see that eating more monounsaturated fats helps increase HDL cholesterol and lower inflammation. Both high and low monounsaturated fat diets lower LDL cholesterol, but only the high-fat diet raises HDL cholesterol. This is one of the main benefits of monounsaturated fats for your heart.
Blood Pressure
Monounsaturated fats can help you manage your blood pressure. Studies show that diets rich in these fats lower both systolic and diastolic blood pressure. For example, people who switched from saturated fats to monounsaturated fats saw their diastolic blood pressure drop by almost 4%. This effect is most noticeable when you keep your total fat intake at a healthy level. If you eat too much fat overall, the benefit may decrease.
When you choose monounsaturated fats instead of saturated fats, you help your blood vessels relax and work better. This makes it easier for your heart to pump blood and lowers your risk of high blood pressure.
Blood Sugar
If you have concerns about blood sugar, monounsaturated fats offer important benefits. Diets high in these fats improve blood sugar control, especially for people with type 2 diabetes. Here are some ways monounsaturated fats help:
Improve glycemic control by lowering fasting blood sugar.
Enhance lipoprotein profiles, which means better cholesterol numbers.
Lower fasting plasma triglycerides and VLDL-cholesterol.
Improve glucose metabolism when you replace saturated fats or carbs with monounsaturated fats.
Do not cause weight gain if you keep your calorie intake steady.
You can support healthy blood sugar levels by choosing foods rich in monounsaturated fats, such as olive oil, nuts, and avocados.
Inflammation
Chronic inflammation can lead to many health problems, including heart disease and arthritis. Monounsaturated fats help your body fight inflammation in several ways:
Shift immune cells to a less inflammatory state.
Lower levels of pro-inflammatory markers like TNF-α, CRP, and IL-6.
Increase anti-inflammatory cytokines, which help your body heal.
Block harmful pathways that cause inflammation.
Protect cells from damage caused by saturated fats.
People who eat diets high in monounsaturated fats, such as the Mediterranean diet, have lower rates of inflammation and related diseases. You can reduce your risk of chronic illness by including more of these healthy fats in your meals.
Weight Management
Monounsaturated fats can help you manage your weight. A clinical trial in women with obesity showed that a diet rich in these fats led to lower body weight, BMI, waist size, and body fat. These changes happened without affecting how many calories the women burned. This means monounsaturated fats help reduce body fat, not just change how your body uses energy.
When you replace saturated fats with monounsaturated fats, you may find it easier to control your weight and reduce belly fat. This is one of the practical benefits of monounsaturated fats for people who want to stay healthy.
Other Potential Benefits
The benefits of monounsaturated fats may go beyond heart health and weight control. Some studies suggest that these fats help protect your brain and support mental health. For example:
Long-term diets high in monounsaturated fats are linked to fewer symptoms of depression.
Animal studies show that these fats protect brain cells and improve mood.
Diets rich in monounsaturated fats may improve brain function and help neurotransmitters work better.
People who eat more monounsaturated fats have a lower risk of depression over time.
The Mediterranean diet, which is high in these fats, is associated with better mental health.
No strong evidence links monounsaturated fats to a lower risk of cancer, but research continues in this area.
Note: While the benefits of monounsaturated fats are clear, eating too much fat of any kind can lead to weight gain. People at risk for gallstones should also watch their fat intake and talk to a doctor if they have concerns.
The benefits of monounsaturated fats make them a smart choice for almost everyone, especially people at risk for heart disease, diabetes, or obesity. By making simple changes to your diet, you can enjoy better health and well-being.
Food Sources

Top Foods
You can find monounsaturated fats in many tasty foods. Olive oil stands out as one of the best sources. One tablespoon of extra virgin olive oil gives you about 9.9 grams of monounsaturated fat. Avocado oil matches olive oil in monounsaturated fat content and works well for cooking at high temperatures. Macadamia nuts and avocados also provide plenty of these healthy fats. Canola oil and walnuts add variety to your choices.
Here is a table showing the monounsaturated fat content in popular foods:
Food | Monounsaturated Fat (per serving) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Olive Oil | 9.9 g / tbsp | Rich in antioxidants |
Avocado Oil | High smoke point, mild flavor | |
Macadamia Nuts | Very high / handful | Nutty taste, heart-healthy |
Avocado | 1 g / slice | Creamy texture, versatile |
Canola Oil | 9 g / tbsp | Good for cooking and baking |
Walnuts | Significant / handful | Also contains polyunsaturated fats |
Tip: Choose oils like olive or avocado for salad dressings and cooking. Snack on nuts or add avocado to sandwiches for a boost of healthy fats.
How to Add to Your Diet
You can easily add more monounsaturated fats to your meals. Swap butter or margarine for olive oil or canola oil when you cook. Use avocado oil for roasting or baking because it handles heat well. Try adding sliced avocado to salads, wraps, or toast instead of cheese or mayonnaise. Snack on a small handful of macadamia nuts or walnuts instead of chips or cookies.
Here are some simple ways to make healthy swaps:
Replace red meat with skinless chicken or fish several times a week.
Use olive or canola oil instead of solid fats in recipes.
Choose low-fat or nonfat dairy products.
You help your heart when you choose plant-based oils and nuts. Scientific studies show that replacing just 5% of your saturated fat intake with monounsaturated fats can lower your risk of heart disease by about 15%. Plant-based sources like olive oil and avocado oil give you the most benefit.
Note: Plant-based fats have a lower environmental impact than animal fats, but growing oil crops can affect land and water use. Choose a variety of sources and enjoy them in moderation for your health and the planet.
You can improve your health by choosing foods rich in monounsaturated fats. The benefits of monounsaturated fats include lower risks of heart disease, stroke, and early death. Even small changes, like swapping butter for olive oil or adding avocados to your meals, make a difference. Health experts recommend replacing saturated fats with monounsaturated fats for better cholesterol and blood sugar. Start today by reviewing your fat choices and making simple swaps for long-term well-being.
FAQ
What is the best way to store oils high in monounsaturated fats?
Store oils like olive or avocado oil in a cool, dark place. Keep the cap tightly closed. Light and heat can make the oil spoil faster. You can use a dark glass bottle for extra protection.
Can you cook with monounsaturated fats at high temperatures?
Yes, you can use oils like avocado oil for high-heat cooking. Olive oil works well for medium heat. These oils stay stable and safe when heated. Always avoid burning the oil.
Are monounsaturated fats safe for children?
Yes, children need healthy fats for growth and brain development. You can add small amounts of olive oil, avocado, or nut butters to their meals. Always watch for allergies when you introduce new foods.
How much monounsaturated fat should you eat daily?
Experts suggest that 15% to 20% of your daily calories come from monounsaturated fats. You can check food labels to track your intake. Choose plant-based oils and nuts for the best results.
Do monounsaturated fats help lower belly fat?
Monounsaturated fats may help reduce belly fat when you replace saturated fats with them. You should also eat a balanced diet and stay active. No single food will target belly fat alone.
See Also
Recognizing Signs And Available Treatments For Duodenal Cancer
An Overview Of Insulinoma And Its Importance Today
Key Symptoms And Treatment Options For Conjunctival Melanoma
A Guide To Symptoms And Care For Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis

