Why Vitamin B2 Matters for Cancer Prevention

You need vitamin B2, also known as riboflavin, to help your body repair DNA and protect your cells from harm. Scientists have found that higher vitamin B2 intake sometimes improves survival rates in certain cancers, such as ovarian and colorectal cancer. However, research shows mixed results, with some studies finding no strong link between vitamin B2 and cancer risk. Cancer and importance of Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) stay connected through the body’s ability to use other B vitamins, which may also affect your cancer risk.
Key Takeaways
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) helps your body repair DNA and protect cells, which may lower cancer risk.
Riboflavin supports energy production, antioxidant defense, and keeps your tissues and mucous membranes healthy.
Getting enough vitamin B2 from foods like milk, eggs, and leafy greens is important because your body cannot store it.
Certain groups, such as pregnant women, older adults, and vegans, may need more vitamin B2 to stay healthy.
Research shows mixed results, but riboflavin works with other B vitamins to support cell health and may reduce some cancer risks.
What Is Vitamin B2?

Riboflavin Basics
Vitamin B2, or riboflavin, is a water-soluble vitamin that your body needs every day. You cannot store much of it, so you must get it regularly from your diet. Riboflavin stands out among the B vitamins because of its special chemical structure. It contains an isoalloxazine ring and a ribityl side chain, which makes it different from other B vitamins like B1, B3, B5, and B6. Chemically, riboflavin is known as 7,8-dimethyl-10-d-ribitylisoalloxazine, with the formula C17H20N4O6. This unique structure allows riboflavin to act as a building block for two important coenzymes: flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). These coenzymes play a key role in energy metabolism and redox reactions in your cells.
Tip: Your body cannot make riboflavin on its own. You need to eat foods rich in vitamin B2 every day to stay healthy.
Role in the Body
Riboflavin helps your body in many ways. It supports energy production, cell growth, and protection against damage. The table below shows some of the main functions of riboflavin:
Biological Function | Description |
|---|---|
Formation of Coenzymes FMN and FAD | Helps create FMN and FAD, which are needed for energy metabolism and redox reactions. |
Energy Metabolism | Supports the production of ATP, the main energy source for your cells. |
Metabolism of Other B Vitamins | Assists in turning other B vitamins, like B3 and B6, into their active forms. |
Maintenance of Homocysteine Levels | Helps control homocysteine, which supports heart health. |
Red Blood Cell Production | Aids in making red blood cells by supporting iron metabolism. |
Antioxidant Activity | Protects your cells from free radical damage by supporting antioxidant enzymes. |
You also rely on riboflavin for healthy skin, hair, and nails. It helps your body grow and repair tissues. Riboflavin supports your nervous system and may help prevent migraines. It even plays a role in keeping your eyes healthy and helps your liver remove toxins. By supporting these vital processes, riboflavin keeps your body strong and helps lower your risk of diseases, including cancer.
Cancer and Importance of Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)

DNA Repair and One-Carbon Metabolism
You need vitamin B2 for healthy DNA. Your cells use riboflavin to make coenzymes called FMN and FAD. These coenzymes help enzymes in your body work properly. One important enzyme is methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase, or MTHFR. This enzyme helps your body use folate, which is another B vitamin. Folate and riboflavin work together in a process called one-carbon metabolism. This process helps your cells make and repair DNA. When you have enough riboflavin, your body can keep your DNA stable and healthy. If you do not get enough, your DNA may not repair itself well, which can raise your risk for cancer.
Riboflavin also helps lower homocysteine, a substance that can damage your blood vessels and DNA if it builds up. Studies show that people with certain genetic changes in MTHFR need more riboflavin to keep homocysteine low. By supporting DNA repair and methylation, riboflavin helps protect you from changes that could lead to cancer. Cancer and importance of Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) often connect through these pathways in your cells.
Note: Riboflavin, folate, and vitamin B6 all work together in your body. They help your cells make new DNA and repair old DNA. This teamwork is important for cancer prevention.
Antioxidant Protection
Your body faces stress from things called free radicals. These are unstable molecules that can damage your cells and DNA. Riboflavin helps your body fight this damage. It supports enzymes that act as antioxidants. These enzymes, like glutathione reductase, use riboflavin to keep your cells safe from harm.
Research shows that riboflavin can lower markers of oxidative stress and inflammation. For example, people with migraines often have high levels of oxidative stress. Riboflavin supplements help reduce these levels. Animal studies also show that riboflavin lowers damage to proteins, fats, and DNA. This protection helps your body stop cancer cells from forming and growing.
Riboflavin also helps your cells make energy. Tumor cells need a lot of energy, so they often have more riboflavin transporters. Scientists use this fact to design new cancer treatments. They attach drugs to riboflavin so the drugs go straight to the tumor cells. This targeted approach may help treat cancer with fewer side effects.
Riboflavin supports your immune system and helps control inflammation.
It can slow down the growth of tumor cells and change how they behave.
Cancer and importance of Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) link together through these antioxidant and immune effects.
Mucous Membrane Defense
Your body uses mucous membranes to protect you from germs and harmful chemicals. These membranes line your mouth, nose, throat, and digestive tract. Riboflavin keeps these barriers strong and healthy. If you do not get enough riboflavin, your mucous membranes can become inflamed or damaged. This makes it easier for carcinogens to enter your body and cause harm.
Studies show that riboflavin deficiency can raise your risk for cancers in places like the mouth, throat, and intestines. Riboflavin helps your cells repair themselves and keeps your tissues healthy. It also works with enzymes that fix DNA and block damage from carcinogens. Cancer and importance of Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) often show up in research about mucous membrane health.
Riboflavin deficiency can weaken your epithelial tissues, making it easier for cancer to start.
Getting enough riboflavin may lower your risk for colorectal, cervical, and lung cancers.
Riboflavin helps your body repair DNA and fight off carcinogens.
Tip: Eating foods rich in riboflavin, like milk, eggs, and leafy greens, helps keep your mucous membranes strong and lowers your cancer risk.
Research Evidence
Cancer Risk Reduction
You may wonder if getting more riboflavin can lower your cancer risk. Some studies show that people who eat more riboflavin have a lower chance of certain cancers. For example, a large study in China found that women who never smoked and ate more riboflavin had a much lower risk of lung cancer. The risk dropped by almost 40% for those with the highest intake compared to the lowest. Another study found that people with higher riboflavin levels in their blood had a lower risk of esophageal cancer, especially in women and older adults. However, not all studies agree. Some research found no strong link between riboflavin and cancers like breast, colorectal, or ovarian cancer. These mixed results show that the connection between riboflavin and cancer is complex.
Key Studies
Researchers have looked at riboflavin and cancer in many ways. Some large studies in China found that higher riboflavin in the blood could raise the risk of colorectal cancer, while others saw a protective effect. Meta-analyses, which combine results from many studies, also show mixed results. Some report that eating more riboflavin lowers the risk of colorectal cancer, but others find no effect. Scientists also study how your genes affect riboflavin’s role. People with certain gene types, like the MTHFR TT genotype, may need more riboflavin to keep their DNA healthy. Riboflavin helps these people lower their homocysteine levels, which may reduce cancer risk. Cancer and importance of Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) often depend on your genes and how your body uses this vitamin.
Limitations
You should know that research on riboflavin and cancer has some limits. Many studies use surveys to ask people what they eat, but people may not remember everything correctly. Some studies only collect data once, so they cannot show cause and effect. Researchers sometimes miss important details, like the type of cancer or other risk factors such as HPV infection. The table below shows some common problems in these studies:
Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
Study Design | Only one time-point, so cannot prove cause and effect |
Recall Bias | People may not remember their diet accurately |
Missing Data | Many participants excluded due to incomplete answers |
Lack of Subtype Data | Cannot tell which cancer types are affected |
Inconsistent Findings | Some studies show benefit, others do not |
Genetic Differences | Not all studies look at how genes change the effect of riboflavin |
Scientists need more long-term studies to understand how riboflavin affects cancer risk. You may see new findings in the future as research continues.
Intake and Sources
Daily Needs
You need vitamin B2 every day because your body cannot store much of it. The amount you need depends on your age, gender, and life stage. The table below shows the recommended daily intake for different groups:
Population Group | Age Range | RDA (mg/day) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Girls | 14-19 years | 1.0 | - |
Boys | 14-19 years | 1.3 | - |
Women | ≥19 years | 1.1 | May not meet needs in malabsorption |
Men | ≥19 years | 1.3 | Same as above |
Pregnant Women | All ages | 1.4 | May require more if multiple fetuses |
Lactating Women | All ages | 1.6 | May require more if nursing multiples |
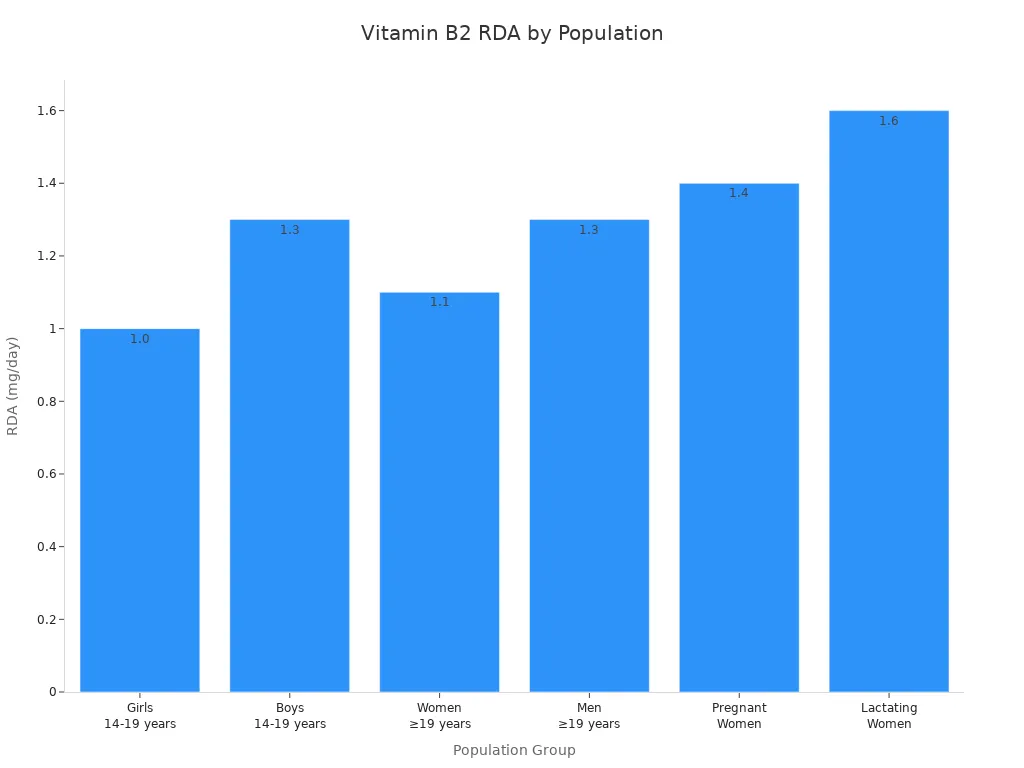
Tip: Pregnant, breastfeeding, and older adults often need more riboflavin.
Deficiency Risk
You can develop riboflavin deficiency if you do not eat enough foods with vitamin B2 or if your body cannot absorb it well. People at higher risk include:
Pregnant and breastfeeding women
Older adults with absorption problems
People with chronic diarrhea or liver disease
Those on dialysis
Vegans who avoid animal products
People with alcohol use disorder
If you lack vitamin B2, you may notice cracks at the corners of your mouth, sore throat, or skin problems. In some countries, riboflavin deficiency is common among refugees and the elderly. Low riboflavin can also affect your memory and thinking skills.
Food Sources
You can get vitamin B2 from many foods. Animal products and some plant foods are good sources. The table below lists foods rich in riboflavin:
Food Item | Riboflavin Content per Serving | % Daily Value (DV) |
|---|---|---|
Beef (Skirt Steak) | 112% DV | |
Fortified Tofu | 1 mg per cup | 76% DV |
Low-Fat Milk | 0.9 mg per 16 oz glass | 69% DV |
Eggs (Large) | 0.3 mg per egg | 20% DV |
You also find riboflavin in leafy greens, mushrooms, and yogurt. Cooking does not destroy much riboflavin, but light can break it down. Store milk and other foods away from light to keep their vitamin B2.
Supplements
You may need a supplement if you cannot get enough riboflavin from food. Supplements work well to raise your blood levels. Doctors sometimes use high doses to treat migraines. Most people do not need large amounts, and your body removes extra riboflavin in urine. Too much can cause yellow urine, diarrhea, or itching. Rarely, you may have an allergic reaction. Always talk to your doctor before starting a supplement, especially if you have health problems or take other medicines.
Vitamin B2 supports your body in many ways that help prevent cancer. You protect your cells from damage, reduce inflammation, and keep your tissues healthy when you get enough riboflavin. The table below shows why scientists believe vitamin B2 matters for cancer prevention:
Reason | Explanation |
|---|---|
Antioxidant Properties | Protects cells from oxidative stress |
Anti-inflammatory Effects | Lowers inflammation linked to cancer |
Cellular Metabolism | Supports healthy cell function and energy |
Activation of B Vitamins | Helps activate vitamin B6 for cell health |
Potential Cancer Risk Drop | May lower risk for some cancers |
Eat a variety of foods rich in vitamin B2. If you worry about your intake or cancer risk, talk to your doctor. Making vitamin B2 a priority can help you stay healthy every day.
FAQ
What happens if you do not get enough vitamin B2?
You may notice cracked lips, sore throat, or skin problems. Your body cannot repair DNA well. This can raise your risk for some cancers. You should eat foods rich in vitamin B2 every day.
Can you get too much vitamin B2 from food?
You cannot get too much vitamin B2 from food. Your body removes extra riboflavin in urine. High doses from supplements may cause yellow urine or mild stomach upset, but food sources are safe.
Does cooking destroy vitamin B2 in foods?
Cooking does not destroy much vitamin B2. However, light can break it down. You should store milk and other foods away from light to keep their vitamin B2 content.
Who needs more vitamin B2?
Pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, older adults, and people with certain health problems need more vitamin B2. If you follow a vegan diet, you should also check your intake.
See Also
Recognizing Symptoms And Treatment Options For Duodenal Cancer
Essential Information On Basaloid Squamous Cell Lung Cancer
Key Facts Everyone Needs To Understand Carcinoid Tumors

