How Diet and Nutrition Help Reduce Cancer Risk

Your daily food choices hold incredible power over your health. Scientific studies reveal that what you eat can significantly influence your risk of developing cancer. For instance, the UK BioBank study found that following dietary guidelines reduced the likelihood of lifestyle-related cancers. Similarly, research highlights that eating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains lowers the risk of head, neck, and colorectal cancers. By embracing healthier habits, you can take control of your well-being and reduce cancer risks. How diet and nutrition play a role in cancer prevention is not just science—it’s a path to a healthier, more vibrant life.
Key Takeaways
The food you eat can affect your cancer risk. Eat more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to stay healthy.
Antioxidants in foods like berries and spinach work better than pills to lower cancer risk.
Add foods with lots of fiber to your meals. Fiber helps digestion and reduces the chance of some cancers, like pancreatic cancer.
Eating mostly plants can help lower cancer risk. Pick whole, natural foods to get important nutrients.
Cut down on processed and red meats. These can raise cancer risk. Try plant-based proteins instead for better health.
How Diet and Nutrition Play a Role in Cancer Prevention

The Science Behind Diet and Cancer
Your diet shapes your health in profound ways. Scientific studies have explored how specific foods and nutrients influence cancer risk. While laboratory research suggests that some compounds in food may either promote or prevent cancer, human studies often show associations rather than direct causation. For example, epidemiological studies link alcohol consumption to higher risks of colon, breast, and liver cancers. On the other hand, diets rich in calcium, dairy, and whole grains are associated with a lower risk of colorectal cancer.
Association with Cancer Risk | Cancer Types | |
|---|---|---|
Alcohol | Positive | Colon, Rectum, Breast, Esophageal, Head and Neck, Liver |
Calcium, Dairy, Whole Grains | Inverse | Colorectal Cancer |
Coffee | Inverse | Liver and Skin Basal Cell Carcinoma |
Understanding these connections empowers you to make informed choices. By prioritizing nutrient-dense foods, you can take steps toward reducing your cancer risk.
Role of Antioxidants in Reducing Cancer Risk
Antioxidants, found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, protect your cells from damage caused by free radicals. This damage can lead to cancer over time. While antioxidants from food sources are beneficial, studies show that supplements may not provide the same protective effects. For instance:
Nine clinical trials found no evidence that antioxidant supplements prevent cancer.
A systematic review concluded that vitamin and mineral supplements do not clearly reduce cancer risk.
Instead of relying on pills, focus on eating colorful fruits and vegetables like berries, spinach, and carrots. These natural sources of antioxidants offer a delicious way to support your health.
Importance of Fiber for Cancer Prevention
Fiber plays a vital role in keeping your digestive system healthy. It also helps lower the risk of certain cancers, particularly pancreatic cancer. Research shows that diets high in fiber are linked to a 46% lower risk of pancreatic cancer. A meta-analysis further revealed that increased fiber intake correlates with a reduced risk, with an odds ratio of 0.54.
Adding fiber-rich foods like whole grains, legumes, and fresh produce to your meals can make a big difference. Not only does fiber support digestion, but it also helps your body eliminate harmful substances that could contribute to cancer.
By understanding how diet and nutrition play a role in cancer prevention, you can take proactive steps to protect your health. Small changes, like eating more fiber and antioxidants, can lead to significant benefits over time.
Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet
Switching to a plant-based diet can transform your health and reduce your cancer risk. This approach emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and legumes while minimizing animal products. By choosing plant-based foods, you provide your body with essential nutrients that protect against cancer.
Plant-based diets are rich in fiber, antioxidants, and phytochemicals. These compounds work together to combat inflammation, neutralize harmful free radicals, and support your immune system. Studies show that following plant-based dietary recommendations can significantly lower cancer risk. For example:
Dietary Recommendation | Cancer Type | Risk Reduction |
|---|---|---|
WCRF/AICR Score Increase | Overall Cancer | 12% |
WCRF/AICR Score Increase | Breast Cancer | 14% |
WCRF/AICR Score Increase | Prostate Cancer | 12% |
These numbers highlight the power of plant-based eating. By increasing your intake of whole, unprocessed plant foods, you can take meaningful steps toward cancer prevention.
You don’t need to overhaul your diet overnight. Start small by adding more vegetables to your meals or swapping meat for plant-based proteins like beans or tofu. Over time, these changes can lead to lasting health benefits. A plant-based diet not only reduces cancer risk but also improves heart health, boosts energy, and supports weight management.
Take control of your health today. Embrace the vibrant colors and flavors of plant-based foods. Each meal becomes an opportunity to nourish your body and protect it from disease. You have the power to make a difference, one bite at a time.
Dietary Habits to Reduce Cancer Risk

Avoiding Processed and Red Meat
Reducing your intake of processed and red meat can significantly lower your cancer risk. Studies show that consuming red meat increases the risk of colorectal, breast, and lung cancers. For example:
Eating red meat raises colorectal cancer risk by 17% (RR = 1.17).
Processed meat consumption increases colorectal cancer risk by 18%.
Total red and processed meat intake is linked to a 26% higher risk of rectal cancer.
Processed meats like bacon, sausage, and hot dogs contain harmful compounds formed during processing. These compounds can damage your cells and lead to cancer over time. Instead of red or processed meats, try plant-based protein sources like beans, lentils, or tofu. These options are not only healthier but also delicious and versatile.
Limiting Sugar and Refined Carbohydrates
High sugar and refined carbohydrate intake can fuel cancer growth by causing spikes in blood sugar and insulin levels. Research highlights that diets high in processed carbohydrates increase prostate cancer risk by 88%. On the other hand, eating low-glycemic index (GI) foods, such as whole grains and legumes, lowers breast cancer prevalence by 67%.
To reduce your cancer risk, choose whole, unprocessed foods over sugary snacks and refined grains. Swap white bread for whole-grain bread or enjoy fresh fruit instead of candy. These small changes can make a big difference in your health.
Evidence Type | Findings | Correlation |
|---|---|---|
Processed Carbohydrates | Increased prostate cancer risk | 88% higher risk |
Low-GI Foods | Lower breast cancer prevalence | 67% lower prevalence |
Legumes | Lower risk of multiple cancers | 32% lower risk |
Incorporating Whole Foods and Healthy Fats
Whole foods and healthy fats provide essential nutrients that protect against cancer. Foods like whole grains, dairy, and coffee are inversely associated with colorectal and liver cancers. For example, studies show that whole grains reduce colorectal cancer risk, while coffee lowers the risk of liver cancer.
Dietary Component | Cancer Type | Association Type |
|---|---|---|
Dairy products | Colorectal cancer | Inversely associated |
Whole grains | Colorectal cancer | Inversely associated |
Coffee | Liver cancer | Inversely associated |
Coffee | Skin basal cell carcinoma | Inversely associated |
Incorporate healthy fats like those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil. These fats support your body’s ability to absorb nutrients and fight inflammation. By focusing on whole foods and healthy fats, you can nourish your body and reduce your cancer risk.
Making these dietary changes may seem challenging at first, but every small step counts. By avoiding processed and red meat, limiting sugar, and embracing whole foods, you take control of your health. How Diet and Nutrition Play a Role in Cancer Prevention becomes clear when you see the positive impact of these habits on your well-being.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight and Avoiding Harmful Substances
Link Between Obesity and Cancer
Your weight plays a crucial role in your overall health, including your cancer risk. Excess body weight has been linked to several types of cancer, such as liver, gallbladder, and endometrial cancers. For example:
From 2011 to 2015, nearly 9.6% of new cancer cases in women and 4.7% in men were attributed to excess weight.
In women, up to 51% of liver or gallbladder cancer cases and 49.2% of endometrial cancer cases were linked to obesity.
In men, 48.8% of liver or gallbladder cancer cases and 30.6% of esophageal adenocarcinoma cases were associated with excess weight.
Even small weight changes can impact your cancer risk. Gaining just 11 pounds during adulthood increases the risk of endometrial cancer by 16% and postmenopausal breast cancer by 6%. On the other hand, intentional weight loss of more than 5% has been shown to lower the risk of obesity-related cancers, including endometrial cancer.
Impact of Alcohol and Tobacco on Cancer Risk
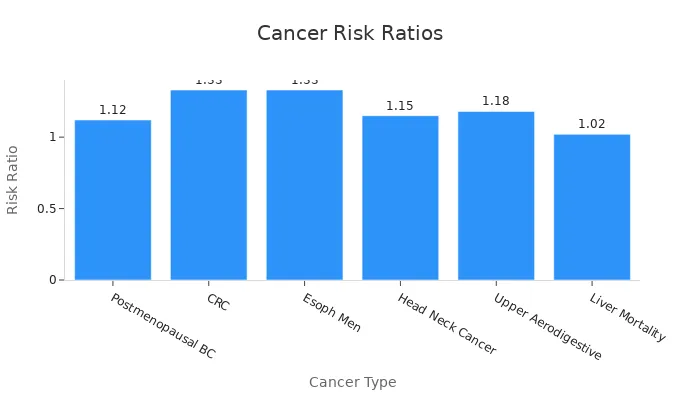
Alcohol and tobacco are two of the most significant contributors to cancer risk. Regular alcohol consumption increases the likelihood of developing cancers such as colorectal, breast, and esophageal cancers.
Cancer Type | 95% Confidence Interval (CI) | |
|---|---|---|
Postmenopausal Breast Cancer | 1.12 | 1.09–1.15 |
Colorectal Cancer (CRC) | 1.33 | 1.22–1.46 |
Esophageal Cancer (Men) | 1.33 | 1.22–1.46 |
Head and Neck Cancer (Oral) | 1.15 | 1.09–1.22 |
Upper Aerodigestive Tract Cancer | 1.18 | 1.11–1.26 |
Liver Cancer Mortality | 1.02 | 1.01–1.03 |
Tobacco use, whether through smoking or chewing, is even more dangerous. It damages your DNA and introduces harmful chemicals into your body, leading to cancers of the lungs, throat, and mouth. Avoiding these substances can dramatically reduce your cancer risk and improve your quality of life.
Strategies for Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is one of the most effective ways to lower your cancer risk. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and mindful eating habits can help you achieve this goal. Consider these strategies:
Follow a plant-based diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Engage in physical activity daily, such as walking, cycling, or yoga.
Monitor portion sizes and avoid overeating.
Studies show that adhering to the World Cancer Research Fund (WCRF) guidelines can reduce cancer risk by 7-30% for specific cancers like breast, colorectal, and gallbladder cancers. Regular exercise not only helps with weight management but also strengthens your immune system and reduces inflammation.
By taking small, consistent steps, you can maintain a healthy weight and protect yourself from cancer. Every choice you make brings you closer to a healthier, more vibrant life.
Exploring Calorie Restriction and Fasting-Mimicking Diets
Benefits of Calorie Restriction for Cancer Prevention
Calorie restriction (CR) involves reducing your daily calorie intake without depriving your body of essential nutrients. This approach has shown promise in lowering cancer risk by influencing biological processes linked to tumor growth. Studies reveal that CR reduces levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), a hormone associated with cancers like breast and thyroid cancer. Lower IGF-1 levels help slow down cell growth and reduce inflammation, creating an environment less favorable for cancer development.
A clinical study published in Cancer Discovery in January 2022 highlighted the impact of calorie restriction on cancer patients. Participants followed a strict regimen, consuming up to 600 calories on the first day and no more than 300 calories for the next four days. The results were remarkable. IGF-1 levels dropped significantly, and immune cells linked to better cancer outcomes increased. These findings suggest that calorie restriction not only reduces cancer risk but also strengthens your body’s natural defenses.
Understanding Fasting-Mimicking Diets
Fasting-mimicking diets (FMDs) are a structured form of calorie restriction designed to mimic the effects of fasting while allowing you to eat small amounts of food. These diets typically involve consuming very low-calorie meals for a few days each month. Unlike traditional fasting, FMDs provide essential nutrients, making them safer and more sustainable.
Research shows that FMDs can reduce cancer-related markers. For example:
Participants consumed up to 600 calories on the first day, followed by 300 calories for the next four days.
IGF-1 levels, a key cancer risk factor, decreased significantly.
Immune cells associated with improved cancer outcomes increased.
By adopting an FMD, you can enjoy the benefits of fasting without the challenges of complete food deprivation.
Precautions and Safe Practices
Before starting calorie restriction or fasting-mimicking diets, consult a healthcare professional. These approaches may not suit everyone, especially if you have underlying health conditions. Gradual changes are key. Begin by reducing portion sizes or skipping snacks rather than diving into a strict regimen.
Stay hydrated and prioritize nutrient-dense foods during fasting periods. Listen to your body. If you feel weak or unwell, adjust your plan. With proper guidance, these dietary strategies can become powerful tools in your journey toward better health.
Actionable Tips for a Cancer-Preventive Diet
Meal Planning and Preparation
Planning your meals can make healthy eating easier and more enjoyable. Start by creating a weekly menu that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. This approach ensures you get the nutrients your body needs to stay strong and reduce cancer risk.
Batch cooking is another great strategy. Prepare meals in advance and store them in portioned containers. This saves time and helps you avoid unhealthy last-minute food choices. For example, cook a large pot of vegetable soup or roast a tray of mixed vegetables to use throughout the week.
Tip: Keep your pantry stocked with staples like beans, lentils, brown rice, and frozen vegetables. These ingredients make it easy to whip up a quick, nutritious meal.
Reading Nutrition Labels and Making Informed Choices
Understanding nutrition labels empowers you to make better food choices. Look for products with minimal added sugars, low sodium, and high fiber content. Pay attention to serving sizes to avoid overeating.
Focus on the ingredient list. Choose items with whole, recognizable ingredients and avoid those with artificial additives or trans fats. For example, when buying bread, opt for one made with whole grains rather than refined flour.
Note: Foods labeled as "low-fat" or "sugar-free" may still contain unhealthy additives. Always check the full label to ensure you're making the best choice.
Staying Motivated and Setting Realistic Goals
Staying motivated is key to maintaining a cancer-preventive diet. Set small, achievable goals, like adding one extra serving of vegetables to your meals each day. Celebrate your progress to stay encouraged.
Surround yourself with support. Share your goals with friends or family, or join a community focused on healthy eating. Tracking your meals in a journal or app can also help you stay on track.
Remember, every positive change you make brings you closer to better health. How Diet and Nutrition Play a Role in Cancer Prevention becomes clearer when you see the impact of your efforts over time.
Your diet holds the power to shape your future health. By making thoughtful food choices, you can significantly reduce your risk of cancer. Research shows that adopting healthier habits can lower the risk of overall cancer by 12%, breast cancer by 14%, and prostate cancer by 12%.
Cancer Type | Risk Reduction (%) |
|---|---|
Overall Cancer | 12 |
Breast Cancer | 14 |
Prostate Cancer | 12 |
Small, consistent changes make the biggest difference. Start by adding more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to your meals. Over time, these steps will lead to lasting benefits. You have the ability to take control of your health, one choice at a time. 🌱
Tip: Every meal is an opportunity to nourish your body and protect it from disease. Take that first step today!
FAQ
What are the best foods to include in a cancer-preventive diet?
Focus on whole, plant-based foods. Include colorful fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and legumes. These provide essential nutrients, antioxidants, and fiber that protect your body from harmful substances and reduce cancer risk.
Tip: Aim for a variety of colors on your plate to maximize nutrient intake. 🌈
Can I still eat meat while reducing my cancer risk?
Yes, but moderation is key. Limit red and processed meats. Instead, choose lean proteins like chicken, fish, or plant-based options such as beans and lentils. These alternatives support your health without increasing cancer risk.
How does sugar affect cancer risk?
High sugar intake can lead to weight gain and insulin spikes, which may increase cancer risk. Replace sugary snacks with fresh fruits or nuts. These options satisfy your cravings while nourishing your body.
Are supplements a good substitute for a healthy diet?
No, whole foods are more effective. Supplements lack the complex nutrients and fiber found in natural foods. Prioritize a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains for optimal health benefits.
Note: Consult your doctor before taking supplements, especially if you have specific health concerns.
How can I stay consistent with a cancer-preventive diet?
Start small. Add one healthy habit at a time, like eating more vegetables or drinking water instead of soda. Celebrate your progress and stay motivated by focusing on the long-term benefits for your health.
Inspiration: Every small step you take brings you closer to a healthier, happier life. 🌟
See Also
Recognizing Symptoms And Causes Of Esophageal Cancer
An In-Depth Overview Of Various Cancer Types
Exploring Symptoms And Causes Associated With Anal Cancer
Identifying Symptoms And Causes Related To Colon Cancer
Comprehending Symptoms And Treatment Options For Duodenal Cancer

