Esophageal Cancer-Understanding Symptoms and Causes
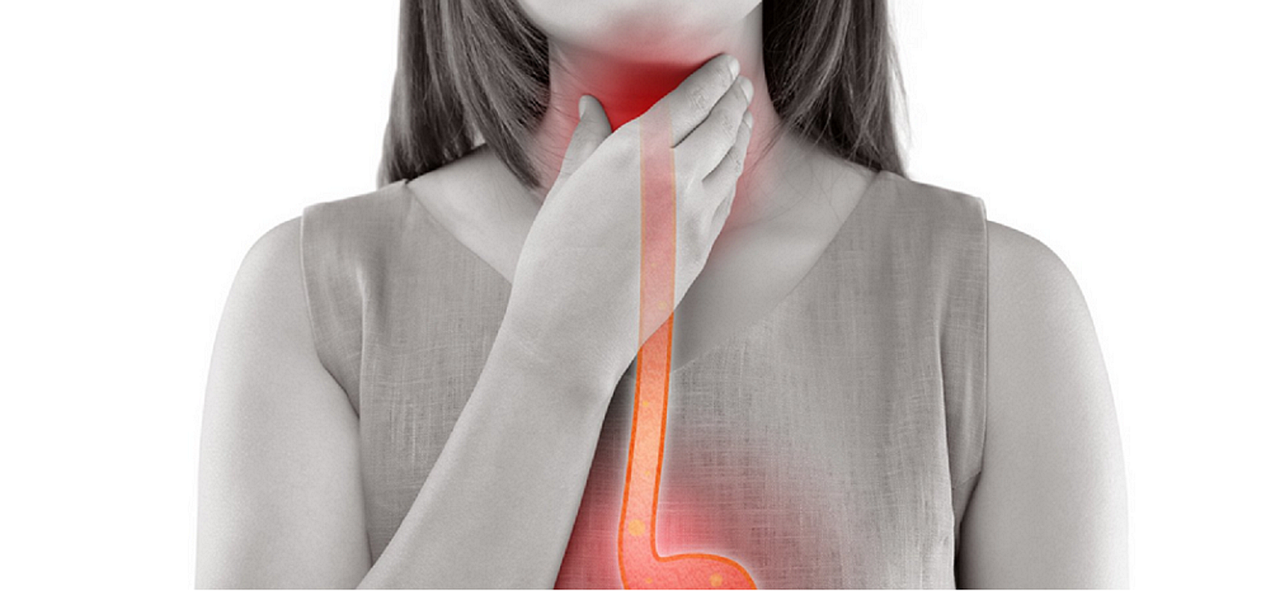
Esophageal cancer often begins with subtle symptoms that you might overlook. Difficulty swallowing or persistent heartburn could be early signs. Globally, this cancer ranks as the 11th most common and the 7th leading cause of cancer-related deaths. It is especially prevalent in regions like eastern Asia and southern Africa. In the United States, esophageal cancer accounts for about 1% of all diagnosed cancers. Early detection is critical, yet only 18.2% of cases are diagnosed at an early stage. When caught early, the five-year survival rate is 48%, compared to just 5% for late-stage diagnoses. Recognizing symptoms early can make a significant difference in outcomes.
Key Takeaways
Know early signs of esophageal cancer, like trouble swallowing and constant heartburn. See a doctor if these last over two weeks.
Realize that habits like smoking and drinking a lot of alcohol raise the chance of getting esophageal cancer. Choosing healthier habits can lower this chance.
Notice that losing weight without trying and a long-lasting cough can mean serious health problems. Talk to a doctor if you have these signs.
Finding cancer early is very important. Regular doctor visits and tests can help treat esophageal cancer better and increase survival chances.
Eat a balanced diet with lots of fruits and vegetables. This can help stop esophageal cancer and make you healthier overall.
What Are the Symptoms of Esophageal Cancer?
Difficulty Swallowing
One of the earliest and most common symptoms of esophageal cancer is difficulty swallowing, also known as dysphagia. You may notice that solid foods, such as bread or meat, feel stuck in your throat. Over time, even liquids can become hard to swallow. This symptom occurs because the tumor narrows the esophagus, making it harder for food and drinks to pass through. Many people initially dismiss this as a minor issue, but persistent trouble swallowing should prompt you to seek medical advice.
Chest Pain or Discomfort
Chest pain or discomfort is another symptom you might experience. This pain often feels like a burning sensation or pressure in the chest. It can occur when swallowing or even at rest. Some people mistake this for heartburn or acid reflux, which delays diagnosis. However, if the pain persists or worsens, it could indicate esophageal cancer. You should not ignore chest pain, especially if it interferes with your daily activities.
Unexplained Weight Loss
Unexplained weight loss is a significant warning sign of esophageal cancer. You might lose weight because swallowing difficulties prevent you from eating enough food. Additionally, the cancer itself can reduce your appetite and increase your metabolism. This combination leads to rapid weight loss, even if you are not trying to shed pounds. Cancer-related inflammation also disrupts your body’s normal processes, breaking down fat and muscle. If you notice sudden weight loss without changes to your diet or exercise routine, consult a healthcare provider.
Persistent Cough or Hoarseness
A persistent cough or hoarseness can signal esophageal cancer, especially if it lasts for weeks without improvement. You might notice your voice becoming raspy or strained. This happens when the tumor irritates the nerves or tissues near your esophagus. Chronic coughing, which doesn’t respond to typical treatments, is another symptom to watch for. While these signs may seem minor, they often indicate underlying issues that require medical attention.
Other less common symptoms include trouble swallowing liquids or saliva. In some cases, you might experience regurgitation of undigested food. These symptoms can disrupt your daily life and should not be ignored.
Other Symptoms
Persistent Indigestion or Heartburn
Frequent indigestion or heartburn that doesn’t improve with over-the-counter remedies could point to esophageal cancer. You might feel a burning sensation in your chest or throat after eating. This occurs because the tumor can cause acid to back up into your esophagus. Over time, this irritation damages the esophageal lining, worsening your symptoms.
Vomiting or Regurgitation
Vomiting or regurgitation of undigested food is another symptom to monitor. You might notice food coming back up shortly after eating. This happens when the tumor blocks the passage of food through your esophagus. In severe cases, vomiting may include blood, which could indicate bleeding in the esophagus.
Fatigue
Fatigue often accompanies esophageal cancer. You might feel unusually tired even after a full night’s sleep. This occurs because the cancer can cause anemia, especially if there’s bleeding in the esophagus. Anemia reduces the oxygen in your blood, leaving you feeling weak and drained. If you experience persistent fatigue alongside other symptoms, consult a healthcare provider.
Note: Symptoms like bone pain or black stools may occur if the cancer spreads or causes internal bleeding. These signs require immediate medical attention.
What Causes Esophageal Cancer?
Lifestyle Factors
Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking significantly increases your risk of esophageal cancer. The longer and more frequently you smoke, the higher your risk becomes. Smokers are twice as likely to develop this cancer compared to non-smokers. Tobacco damages the cells lining your esophagus, making them more vulnerable to cancerous changes. If you combine smoking with alcohol consumption, your risk multiplies. Studies show that smokers who drink heavily face up to eight times the risk of developing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma compared to non-smokers.
Heavy Alcohol Consumption
Drinking alcohol excessively also raises your risk of esophageal cancer, particularly squamous cell carcinoma. Alcohol irritates the esophagus lining, leading to inflammation and cell damage. Over time, this damage can result in cancer. The combination of alcohol and smoking is especially harmful, as alcohol makes it easier for tobacco carcinogens to penetrate the esophagus lining.
Medical Conditions
Chronic Acid Reflux (GERD)
If you experience frequent acid reflux, you may have a higher risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma. GERD causes stomach acid to flow back into your esophagus, damaging its lining. Over time, this damage can lead to Barrett’s esophagus, a condition where normal cells are replaced by abnormal ones. These abnormal cells increase your likelihood of developing cancer.
Barrett’s Esophagus
Barrett’s esophagus is a serious complication of GERD. In this condition, chronic acid exposure changes the esophagus lining, creating pre-cancerous cells. If left untreated, these cells can progress to esophageal cancer. Regular monitoring and treatment can help reduce this risk.
Other Risk Factors
Obesity
Obesity contributes to esophageal cancer by increasing your risk of GERD. Excess weight puts pressure on your stomach, causing acid to back up into your esophagus. This repeated exposure to acid can lead to Barrett’s esophagus and, eventually, cancer.
Poor Diet
A diet high in processed meats and low in fruits and vegetables may elevate your risk of esophageal cancer. Processed meats contain carcinogens that can damage your esophagus lining. On the other hand, a diet rich in fruits and vegetables provides protective nutrients that lower your risk.
Genetic Predisposition
Although rare, genetic factors can play a role in esophageal cancer. Conditions like Tylosis, caused by a mutation in the RHBDF2 gene, significantly increase your risk. Certain chromosomal abnormalities, such as those on 5q11 and 6p21, have also been linked to this cancer.
Tip: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including quitting smoking, limiting alcohol, and maintaining a balanced diet, can help reduce your risk of esophageal cancer.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Recognizing Warning Signs
Persistent Symptoms That Worsen Over Time
Certain symptoms should prompt you to seek medical attention, especially if they persist or worsen. These include trouble swallowing, chest pain, and unexplained weight loss. You might also notice hoarseness, chronic coughing, or vomiting. In advanced cases, symptoms like bone pain or bleeding into the esophagus may occur. Bleeding can lead to anemia, causing fatigue and weakness. Pay close attention to these signs, as they often indicate a serious underlying condition.
Symptoms That Interfere With Eating or Daily Life
When symptoms begin to disrupt your daily routine, it’s time to act. Difficulty swallowing can make eating uncomfortable or even impossible. Vomiting or regurgitation may prevent you from keeping food down. If you experience these issues, your body may not get the nutrients it needs, leading to weight loss and fatigue. These disruptions can significantly impact your quality of life, so don’t delay in consulting a healthcare provider.
Importance of Early Detection
Benefits of Early Diagnosis
Early detection of esophageal cancer can improve your chances of successful treatment. Identifying the disease in its initial stages allows for less invasive interventions and better outcomes. Research shows that screening programs for upper gastrointestinal cancers can reduce mortality rates by up to 57%. Early diagnosis also enables doctors to monitor and treat pre-cancerous conditions, potentially preventing cancer from developing.
Screening and Diagnostic Tests
Doctors use several effective methods to detect esophageal cancer early. The most common is an upper gastrointestinal endoscopy with a biopsy, which allows direct visualization and tissue sampling. Endoscopic mucosal iodine staining enhances detection by highlighting abnormal areas. Liquid biopsies, which identify tumor cells or DNA in the blood, offer a non-invasive option. Emerging technologies like AI-assisted diagnostic systems and exhaled gas marker analysis show promise for improving accuracy and convenience. Discuss these options with your doctor to determine the best approach for your situation.
Esophageal cancer symptoms, such as difficulty swallowing or chest pain, demand your attention. Ignoring these signs can delay diagnosis and reduce treatment success. Understanding the causes, including lifestyle factors like smoking and medical conditions such as GERD, empowers you to take preventive steps.
You can lower your risk by adopting healthy habits:
Eat a diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
Early detection improves survival rates significantly. For localized esophageal cancer, the five-year survival rate is 48%, compared to just 5% for distant stages. If symptoms persist or worsen, consult a healthcare provider promptly.
Tip: Regular check-ups and managing reflux conditions can help prevent complications like Barrett’s esophagus.
FAQ
What are the early warning signs of esophageal cancer?
Early signs include difficulty swallowing, persistent heartburn, and unexplained weight loss. You might also notice hoarseness or a chronic cough. These symptoms often start subtly but worsen over time.
Tip: If you experience these symptoms for more than two weeks, consult a healthcare provider.
Can esophageal cancer be prevented?
You can reduce your risk by avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol. Eating a diet rich in fruits and vegetables also helps. Maintaining a healthy weight and managing acid reflux conditions like GERD are additional preventive measures.
How is esophageal cancer diagnosed?
Doctors use endoscopy to examine your esophagus and take a biopsy if needed. Other tests include imaging scans like CT or PET scans. Blood tests and liquid biopsies may also help detect cancer markers.
Is esophageal cancer hereditary?
While most cases are not hereditary, certain genetic conditions like Tylosis can increase your risk. If you have a family history of esophageal cancer, discuss screening options with your doctor.
What treatments are available for esophageal cancer?
Treatment depends on the stage. Options include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted therapies. Early-stage cancer may only require minimally invasive procedures. Advanced cases often need a combination of treatments.
Note: Early detection improves treatment success rates significantly.
---
ℹ️ Explore more: Read our Comprehensive Guide to All Known Cancer Types for symptoms, causes, and treatments.
See Also
Exploring Anal Cancer: Symptoms And Underlying Causes
Duodenal Cancer: Key Symptoms And Available Treatments
Colon Cancer: Identifying Symptoms And Their Causes
Bladder Cancer: Recognizing Symptoms And Their Causes
Breast Cancer: Understanding Symptoms And Contributing Factors

