Tracing the Journey of Cancer Surgery from Tradition to Robotics
Cancer surgery has experienced a significant transformation, aptly described in 'The Evolution of Surgery in Cancer Care: From Scalpel to Robots.' Early methods relied on open surgery, which often caused considerable trauma and extended recovery times. However, modern advancements have introduced robotic systems that revolutionize surgical precision and patient care. For example, the da Vinci Si surgical system, launched in 2009, has improved outcomes in procedures such as robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Studies have shown better recovery rates and fewer complications compared to traditional methods. Although robotic techniques may come with higher costs, they have successfully shortened operation times and enhanced safety. This evolution highlights the essential role of technology in reshaping cancer treatment.
Key Takeaways
Cancer surgery has changed from old methods to robotic systems. These systems improve accuracy and patient care.
Robotic surgeries help patients recover faster with fewer problems. Many patients now choose this option.
The da Vinci system is a leader in robotic surgery. It improves results for surgeries like prostate removal.
New tech like AI is changing robotic surgery. It helps make treatments more personal and decisions better.
Making robotic surgery available in poor areas is important. This ensures everyone can use these advanced methods.
The Evolution of Surgery in Cancer Care: From Scalpel to Robots

Early Cancer Surgery Techniques
The origins and role of open surgery in cancer treatment.
Open surgery marked the beginning of cancer treatment. Surgeons relied on this method to remove tumors directly, often through large incisions. This approach allowed them to access and visualize the affected area fully. For many years, open surgery remained the primary option for treating cancers like breast, lung, and colorectal. It played a crucial role in saving lives, especially when early detection made complete tumor removal possible.
However, not all patients received surgery. A study revealed that over 4% of women with non-metastatic breast cancer in the U.S. did not undergo surgery. Between 2004 and 2009, the percentage of patients avoiding surgery decreased from 4.7% to 3.5%. By 2016, this number rose to 5.3%. Reasons included patient refusal, contraindications due to health risks, or surgery not being part of the initial treatment plan. Despite its importance, open surgery had limitations that led to the development of less invasive techniques.
Challenges and limitations of traditional surgical methods.
Traditional open surgery posed significant challenges. Large incisions often caused severe pain, increased blood loss, and higher risks of infection. Recovery times were lengthy, leaving patients vulnerable to complications. Additionally, the precision of tumor removal was limited, which sometimes affected long-term outcomes. For example, patients undergoing open prostate surgery often faced issues like urinary incontinence and sexual dysfunction. These challenges highlighted the need for advancements in surgical techniques, paving the way for minimally invasive methods.
The Shift to Minimally Invasive Surgery
Introduction and impact of laparoscopic techniques.
The introduction of laparoscopic surgery revolutionized cancer care. This technique used small incisions, a camera, and specialized instruments to perform procedures. It reduced trauma to the body, leading to faster recovery and fewer complications. For instance, minimally invasive surgery for gynecological cancers resulted in shorter hospital stays and less blood loss. Similarly, colorectal cancer surgeries achieved better outcomes due to improved precision. These advancements demonstrated the potential of smaller incisions in enhancing patient care.
Transitioning from open to less invasive procedures.
The transition from open to minimally invasive surgery marked a significant milestone in cancer treatment. Robotic systems further enhanced this shift by offering greater precision and control. Robotic prostatectomies, for example, reduced blood loss and improved functional outcomes compared to traditional methods. Patients experienced fewer complications and faster recoveries. This evolution in surgical techniques underscored the importance of innovation in improving cancer care. The journey from open surgery to minimally invasive methods laid the foundation for the rise of robotic systems.
The Rise of Robotic Systems in Cancer Surgery
Pioneering Robotic-Assisted Surgery
The development and adoption of the da Vinci system.
The da Vinci surgical system revolutionized cancer surgery by introducing robotic-assisted techniques. Developed by Intuitive Surgical, this system gained FDA approval in 2000. It allowed surgeons to perform complex procedures with enhanced precision and control. The da Vinci system featured robotic arms equipped with surgical instruments and a high-definition 3D camera. Surgeons operated these arms using a console, ensuring greater accuracy in delicate surgeries. This innovation marked a turning point in cancer care, reducing complications and improving patient outcomes.
Key milestones in robotic surgery for cancer care.
Robotic-assisted surgery achieved several milestones during its pioneering phase. The introduction of the da Vinci Si system in 2009 improved controllability and safety. Robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) became a standard procedure for localized prostate cancer, offering a 1.35 times higher continence rate after 12 months compared to traditional methods. Key performance indicators, such as positive surgical margins and biochemical recurrence rates, highlighted the system's effectiveness. These advancements demonstrated the potential of robotics in transforming cancer surgery.
How Robotic Systems Enhance Surgery
Features like 3D visualization and enhanced dexterity.
Robotic systems offer features that enhance surgical precision. High-definition 3D visualization provides surgeons with a detailed view of the surgical site, improving accuracy. Robotic arms mimic human movements but with greater dexterity, allowing precise navigation in narrow anatomical spaces. These features minimize damage to surrounding tissues, reducing complications and improving recovery times.
The role of surgeons in robotic-assisted procedures.
Surgeons play a crucial role in robotic-assisted procedures. They control the robotic arms from a console, ensuring every movement aligns with the surgical plan. Advanced robotic integration standardizes procedures, reducing preventable errors and enhancing operating room efficiency. While robots assist with precision, the surgeon's expertise remains vital in achieving optimal outcomes.
Expanding Applications in Cancer Care
Types of cancer surgeries performed with robotic systems.
Robotic systems are now used in various cancer surgeries. For prostate cancer, robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy has become the standard, enhancing precision and reducing complications. Gynecological cancers benefit from robotic hysterectomies and lymph node dissections, which result in less blood loss and quicker recovery. These applications highlight the versatility of robotic systems in cancer care.
Increasing adoption across hospitals and specialties.
The adoption of robotic systems in cancer surgery continues to grow. A 2022 report revealed that 1.5 million surgeries were performed using the da Vinci system, marking a 15% increase from the previous year. Hospitals worldwide have embraced robotic platforms for thyroid, prostate, and general surgeries. The table below illustrates adoption rates across different types of cancer surgeries:
Statistic Description | Value | Year |
|---|---|---|
Usage for thyroid cancer | 38% | 2023 |
Usage for prostate cancer | 27.8% | 2023 |
Surgeries using da Vinci system | 1.5M | 2022 |
Increase from previous year | 15% | 2022 |
Increase in robotic surgery adoption | 8.8% | First four years post-introduction |
Decrease in laparoscopic procedures | 53.2% to 51.3% | First four years post-introduction |
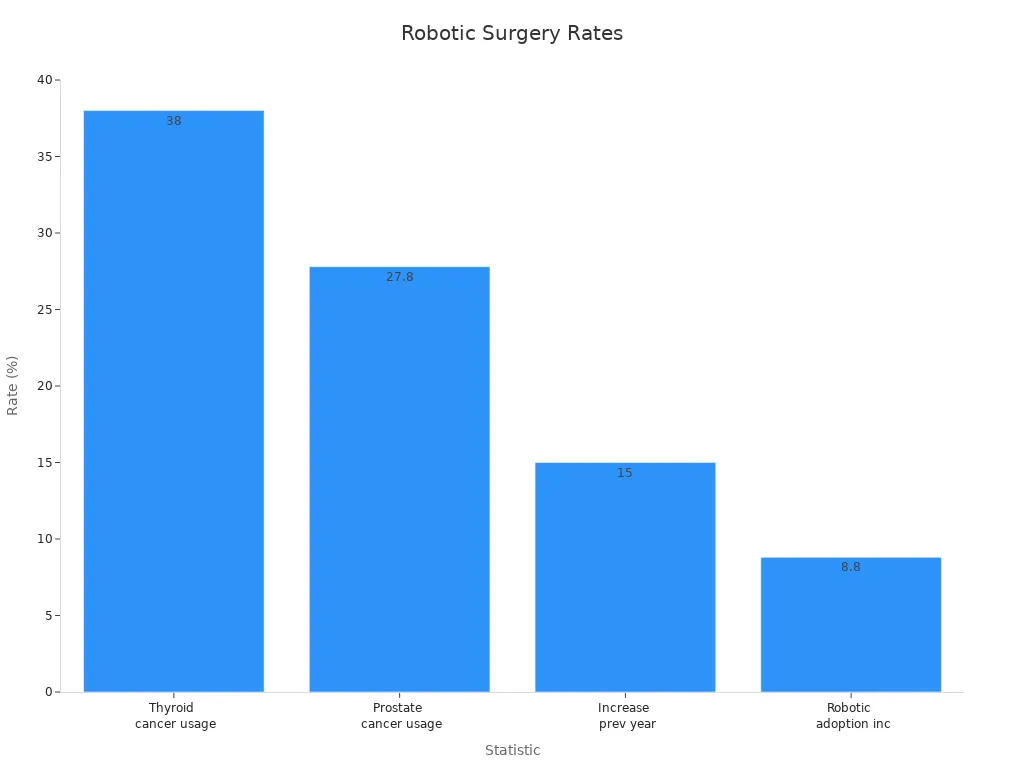
These statistics underline the growing preference for robotic systems in cancer care, driven by their ability to improve precision and patient outcomes.
Benefits and Challenges of Robotic Cancer Surgery
Advantages of Robotic Surgery
Enhanced precision and reduced surgical trauma.
Robotic systems bring unparalleled precision to cancer surgery. Their advanced 3D visualization and dexterous robotic arms allow surgeons to navigate complex anatomical structures with ease. This precision minimizes damage to surrounding tissues, reducing surgical trauma. For example, robotic surgery has been shown to facilitate higher-quality tissue retrieval, particularly in challenging cases like low rectal tumors. Patients benefit from fewer complications, which contributes to better overall outcomes.
Shorter recovery times and improved patient outcomes.
Robotic-assisted procedures often lead to faster recovery. Patients typically experience shorter hospital stays due to reduced postoperative complications. Studies have also noted lower rates of conversion to open surgery compared to laparoscopy. These factors enhance patient outcomes, making robotic surgery a preferred option for many. Additionally, improvements in specimen retrieval quality further highlight the effectiveness of robotic systems in cancer care.
Patients undergoing robotic surgery often recover faster, spending less time in the hospital.
Postoperative complications are significantly reduced, improving long-term health.
Robotic systems ensure higher-quality tissue retrieval, especially in complex surgeries.
Challenges and Limitations
High costs and accessibility issues.
Despite its benefits, robotic surgery comes with high costs. The initial investment in robotic systems is substantial, making them less accessible to smaller hospitals. Maintenance and technical support add to the financial burden. While robotic systems may offer long-term cost savings through reduced complications and shorter hospital stays, the upfront expenses remain a barrier for widespread adoption.
The learning curve for surgeons and technical constraints.
Surgeons require extensive training to master robotic systems. The learning curve can delay the integration of robotic surgery into clinical practice. Additionally, technical issues, such as system malfunctions, can disrupt procedures. Maintenance requirements further complicate the adoption process. These challenges highlight the need for ongoing training and support to maximize the potential of robotic systems.
Aspect | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
Surgical Outcomes | Learning curve for surgeons | |
Costs | Potential long-term cost savings | High initial investment in robotic systems |
Procedural Efficiency | Enhanced precision in surgery | Technical issues and maintenance requirements |
While robotic surgery offers significant advantages, addressing its challenges is essential for broader implementation in cancer care.
The Future of Robotic Cancer Surgery
Emerging Technologies in Robotic Systems
AI integration and machine learning in surgical tools.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are transforming robotic cancer surgery. These technologies enable robotic systems to analyze vast amounts of data, improving decision-making during procedures. For instance, AI algorithms can identify tumor boundaries more accurately, guiding surgeons in real time. Machine learning also enhances robotic precision by predicting potential complications based on patient-specific data. These advancements reduce errors and improve surgical outcomes, making procedures safer and more effective.
AI-powered tools also assist in preoperative planning. By analyzing imaging data, these systems create detailed surgical maps, helping surgeons strategize before entering the operating room. This level of preparation minimizes risks and ensures better results. As AI continues to evolve, its role in robotic surgery will likely expand, offering even greater benefits to patients and healthcare providers.
Development of smaller, more versatile robotic platforms.
The development of compact robotic platforms is another exciting advancement. Smaller systems allow surgeons to perform procedures in tight spaces, such as the thoracic cavity, with greater ease. These platforms also reduce the physical footprint in operating rooms, making them more accessible to hospitals with limited space. Versatile designs enable the use of robotic systems across a broader range of cancer surgeries, from colorectal to gynecological procedures. This adaptability ensures that more patients can benefit from robotic-assisted techniques.
Advancements in Cancer Treatment
Personalized robotic surgery tailored to patients.
Personalized medicine is shaping the future of robotic cancer surgery. By integrating patient-specific data, robotic systems can tailor procedures to individual needs. For example, preoperative imaging and genetic information help customize surgical approaches, ensuring optimal outcomes. This level of personalization enhances precision and reduces the risk of complications. It also aligns with the broader trend of individualized cancer care, where treatments are designed to meet the unique requirements of each patient.
Expanding access to underserved regions.
Expanding access to robotic surgery in underserved regions remains a critical goal. Many rural and low-income areas lack the resources to adopt advanced surgical technologies. However, innovations like tele-surgery and cost-effective robotic platforms are bridging this gap. Tele-surgery allows experienced surgeons to operate remotely, bringing high-quality care to patients in remote locations. Additionally, the development of affordable robotic systems ensures that more hospitals can offer these life-saving procedures. These efforts aim to make robotic cancer surgery accessible to all, regardless of geographic or economic barriers.
Robotic-assisted surgery is increasingly utilized in colorectal and thoracic cancer procedures. It enhances surgical capabilities, reduces postoperative complications, and improves recovery times. High-definition 3D vision systems further aid surgeons by providing better visualization, reducing the risk of damage to critical structures.
The journey of cancer surgery has progressed from traditional open methods to advanced robotic systems. These innovations have transformed patient care by enhancing precision and reducing surgical trauma. Robotic-assisted procedures, particularly for thoracic malignancies like lung cancer, offer less invasive alternatives. Patients experience decreased pain, quicker recovery, and fewer complications.
The future of robotic cancer surgery holds immense promise. Emerging technologies, such as AI and personalized approaches, aim to revolutionize treatment further. These advancements could make high-quality care accessible to more patients, reshaping the landscape of cancer treatment globally.
FAQ
What is robotic cancer surgery?
Robotic cancer surgery uses advanced robotic systems to assist surgeons in performing precise procedures. These systems include robotic arms, cameras, and consoles that enhance visualization and dexterity. Surgeons control the robots, ensuring accuracy in removing tumors while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
How does robotic surgery differ from traditional methods?
Robotic surgery offers greater precision and smaller incisions compared to traditional open surgery. It reduces blood loss, pain, and recovery time. Unlike laparoscopic surgery, robotic systems provide 3D visualization and enhanced dexterity, allowing surgeons to perform complex procedures more effectively.
Are robotic surgeries safe for cancer treatment?
Robotic surgeries are considered safe and effective for many cancer treatments. Studies show fewer complications and better outcomes compared to traditional methods. However, the success of robotic surgery depends on the surgeon's expertise and the type of cancer being treated.
What types of cancer can robotic systems treat?
Robotic systems are commonly used for prostate, gynecological, colorectal, and thoracic cancers. They are also expanding into thyroid and head-and-neck cancer surgeries. Their versatility allows surgeons to address tumors in hard-to-reach areas with improved precision.
Is robotic surgery widely available?
Robotic surgery is growing in availability but remains limited in some regions due to high costs. Larger hospitals and specialized centers often offer these procedures. Efforts to develop affordable systems aim to expand access to underserved areas.
Robotic surgery continues to evolve, making it a promising option for cancer care.
See Also
Recognizing Symptoms And Treatments For Duodenal Cancer
Identifying Symptoms And Treatment Options For Conjunctival Melanoma
Key Features And Insights Into Cholangiocarcinoma Explained

