How Weight Management Can Help Lower Your Cancer Risk

Managing Weight for Cancer Prevention: Guidelines and Tips begins with taking control of your health. Managing your weight reduces the risk of hormone imbalances, chronic inflammation, and insulin resistance—three factors linked to cancer development. Studies show that weight loss lowers levels of insulin and estrogen, hormones associated with cancer risk. For example, bariatric surgery patients experienced a 32% drop in cancer risk and a 48% lower chance of cancer-related death. Excess weight contributes to nearly 10% of new cancer cases in women. By focusing on managing weight for cancer prevention, you can protect your body and embrace a healthier future.
Key Takeaways
Keeping a healthy weight can lower cancer risk by balancing hormones like insulin and estrogen.
Eating more fruits, vegetables, and plant-based foods can reduce swelling and help with weight loss, lowering cancer risk.
Exercising often, like doing cardio or lifting weights, helps you stay fit and lowers cancer risk.
Eating meals at regular times and getting enough sleep can improve how your body uses energy and help you manage weight.
Losing even a little weight can make you healthier, reduce swelling, and boost your immune system.
The Link Between Weight and Cancer Risk

How Excess Weight Contributes to Cancer
Hormonal Imbalances
Excess weight can disrupt your body's natural hormone balance. Fat tissue produces estrogen, and higher levels of this hormone have been linked to cancers like breast and endometrial cancer. Additionally, obesity can increase insulin levels, which may promote the growth of certain tumors. By managing your weight, you can help regulate these hormones and reduce your cancer risk.
Chronic Inflammation
Carrying extra weight often leads to chronic inflammation. This persistent state of inflammation can damage cells and create an environment where cancer thrives. Research shows that individuals with obesity tend to have less diverse gut microbiota, which contributes to inflammation and altered metabolism. Reducing your weight can lower inflammation and protect your cells from harm.
Insulin Resistance
Excess weight can make your body less responsive to insulin, leading to insulin resistance. This condition not only increases your risk of diabetes but also fuels cancer growth by promoting cell division. Stabilizing your weight helps improve insulin sensitivity, reducing your risk of both diabetes and cancer.
Scientific Evidence on Weight and Cancer
Research Studies on Obesity and Cancer
Studies have shown a strong link between obesity and cancer risk. For example:
About 5% of cancers in men and 11% in women in the U.S. are linked to excess body weight.
Obesity contributes to approximately 7% of all cancer deaths.
Certain cancers, like liver and endometrial cancer, have obesity-related risks as high as 51% and 49.2%, respectively.
Findings on Weight Loss and Cancer Risk Reduction
Losing weight can significantly lower your cancer risk. A study from 2011 to 2015 found that excess weight was responsible for over 37,000 new cancer cases in men and nearly 75,000 in women. By achieving a healthy weight, you can reduce your chances of developing these cancers.
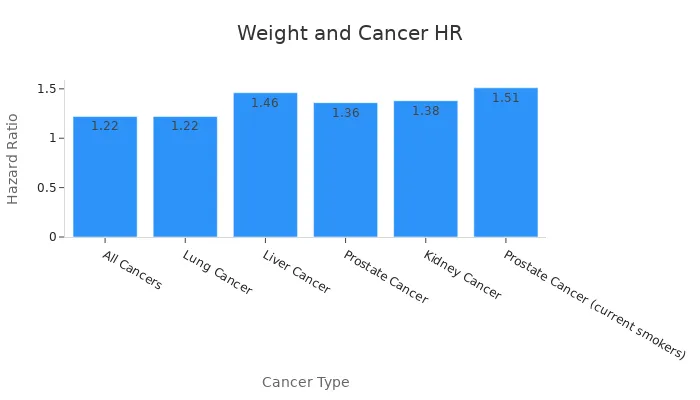
Cancer Type | Hazard Ratio (HR) | 95% Confidence Interval (CI) |
|---|---|---|
All Cancers | 1.15–1.30 | |
Lung Cancer | 1.22 | 1.07–1.39 |
Liver Cancer | 1.46 | 1.19–1.81 |
Prostate Cancer | 1.36 | 1.15–1.62 |
By taking steps to manage your weight, you can protect yourself from these risks and embrace a healthier future.
Types of Cancers Associated with Obesity
Common Cancers Linked to Excess Weight
Breast Cancer
Excess weight, especially after menopause, increases your risk of breast cancer. Fat tissue produces estrogen, and higher levels of this hormone can fuel the growth of breast tumors. Studies show that maintaining a healthy weight reduces this risk significantly. By focusing on weight management, you can take an active step toward protecting your health.
Colorectal Cancer
Obesity raises your chances of developing colorectal cancer by about 30%. This happens because excess weight can lead to chronic inflammation and insulin resistance, both of which promote abnormal cell growth in the colon and rectum. Losing weight can help lower these risks and improve your overall digestive health.
Endometrial Cancer
Endometrial cancer risk increases dramatically with obesity. Women with severe obesity face a sevenfold higher risk compared to those with a healthy weight. Even moderate weight loss can reduce this risk, giving you more control over your health.
Other Cancers with Obesity Links
Pancreatic Cancer
Obesity increases your risk of pancreatic cancer by 1.5 times. This type of cancer is aggressive, but you can reduce your risk by maintaining a healthy weight and adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
Kidney Cancer
Excess weight doubles your risk of kidney cancer. Fat tissue can alter hormone levels and create an environment where cancer cells thrive. By managing your weight, you can protect your kidneys and reduce this risk.
Esophageal Cancer
Severe obesity raises your risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma nearly fivefold. This cancer is linked to chronic acid reflux, which is more common in individuals with excess weight. Losing weight can help alleviate reflux symptoms and lower your cancer risk.
Obesity-Related Cancer Statistics
Global and U.S. Data
In 2012, excess body weight caused 3.9% of all cancers worldwide, equating to 544,300 cases.
Women experienced a greater impact, with 368,500 cases compared to 175,800 in men.
High-income countries reported the highest percentages, with obesity-related cancers accounting for up to 8% of cases.
Trends in Cancer and Obesity Rates
The incidence of obesity-related cancers is rising, particularly among younger women and Hispanic women. In the U.S., 9.5% of cancers are linked to obesity. Preventing excess weight can reduce your risk of several cancers, including colorectal, breast, and pancreatic cancers.
Age Group | Trend in Obesity-Associated Cancers | Demographic Focus |
|---|---|---|
Women 20-49 years | Rising incidence | Younger women |
Hispanic Women | Rising incidence | Specific demographic |
By managing your weight, you can take control of your health and reduce your risk of these cancers. Small, consistent changes in your lifestyle can make a big difference.
Managing Weight for Cancer Prevention: Guidelines and Tips
Healthy Eating Strategies
Focus on Plant-Based Foods
Incorporating more plant-based foods into your diet can significantly reduce your cancer risk. These foods are rich in fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants, which protect your cells and support overall health. Studies show that nearly 25% of cancer cases could be prevented through diet and nutrition alone. Vegans have the lowest cancer rates, followed by vegetarians. High-fiber diets, often found in plant-based eating, lower the risk of breast and colorectal cancers. By filling your plate with fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, you take a powerful step toward managing weight for cancer prevention.
Reduce Processed and Fried Foods
Processed and fried foods often contain unhealthy fats, sugars, and additives that contribute to weight gain and inflammation. These factors increase your cancer risk. Reducing your intake of these foods can help you maintain a healthy weight and lower your risk of chronic diseases. Instead of reaching for chips or sugary snacks, opt for whole, nutrient-dense options like nuts, seeds, or fresh fruit. Small changes in your diet can make a big difference in your health.
Physical Activity Recommendations
Benefits of Aerobic Exercise
Aerobic exercise, such as walking, running, or cycling, plays a crucial role in managing weight for cancer prevention. Regular physical activity reduces your risk of several cancers, including bladder, breast, and colon cancer. For example, a 2016 meta-analysis found that women who were the most active had a 12–21% lower risk of breast cancer. Similarly, individuals engaging in high levels of physical activity had a 19% lower risk of colon cancer. By staying active, you not only manage your weight but also strengthen your body against cancer.
Strength Training for Weight Control
Strength training builds muscle, boosts metabolism, and helps you maintain a healthy weight. This type of exercise also improves bone density and overall strength, making it an excellent addition to your routine. Incorporating activities like weightlifting or resistance band exercises twice a week can enhance your weight management efforts and support cancer prevention. You don’t need to start heavy—small, consistent efforts lead to lasting results.
Lifestyle Changes for Long-Term Success
Establishing Consistent Meal Routines
Creating a consistent meal schedule helps regulate your metabolism and prevents overeating. Skipping meals or eating at irregular times can lead to weight gain and disrupt your body’s natural rhythms. By planning your meals and snacks, you can make healthier choices and stay on track with your weight management goals. This simple habit supports your efforts to reduce cancer risk and improve overall well-being.
Prioritizing Sleep and Stress Management
Quality sleep and stress management are essential for maintaining a healthy weight. Poor sleep disrupts hormones that regulate hunger, leading to overeating and weight gain. Chronic stress triggers the release of cortisol, which can increase fat storage. Prioritize 7–9 hours of sleep each night and practice stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing. These habits not only help you manage your weight but also promote a healthier, more balanced life.
Medical Interventions for Weight Management
Weight-Loss Medications
Weight-loss medications can be a powerful tool in your journey to better health. These medications work by suppressing appetite, reducing fat absorption, or altering hunger hormones. They are especially effective when combined with healthy eating and regular exercise. For individuals struggling with obesity, these medications can help you achieve a healthier weight and lower your cancer risk.
Clinical trials have shown that weight-loss medications contribute to reducing the risk of cancers such as liver, colorectal, and kidney cancer. By managing your weight with these tools, you can take a proactive step toward cancer prevention. Always consult your healthcare provider to determine if these medications are right for you.
Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery offers a life-changing solution for individuals with severe obesity. This procedure reduces the size of your stomach, helping you eat less and lose weight effectively. Beyond weight loss, bariatric surgery has been linked to significant reductions in cancer risk.
Type of Cancer | Risk Reduction Observed |
|---|---|
Liver | Yes |
Colorectal | Yes |
Kidney and Urinary Tract | Yes |
Esophageal | Yes |
Lung | Yes |
The benefits of bariatric surgery extend beyond cancer prevention. Many patients experience improved quality of life, better mobility, and reduced risk of other obesity-related conditions. If you’re considering this option, speak with a specialist to explore how it can support your goals for managing weight for cancer prevention: guidelines and tips tailored to your needs.
💡 Tip: Medical interventions are most effective when paired with a commitment to healthy lifestyle changes.
Benefits of Weight Loss for Cancer Prevention

Hormonal and Metabolic Improvements
Lower Estrogen Levels
Losing weight helps lower estrogen levels, especially in individuals with excess body fat. Fat tissue produces estrogen, which can fuel the growth of certain cancers, such as breast and endometrial cancer. By reducing body fat, you can decrease estrogen production and lower your cancer risk. Studies show that intentional weight loss of more than 5% can significantly reduce these risks. This small change can make a big difference in your health.
Stabilized Insulin Levels
Weight loss improves insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of insulin resistance—a condition linked to cancer growth. Research highlights that individuals who lose weight experience a doubling of peripheral insulin sensitivity within a year. This improvement not only lowers cancer risk but also enhances overall metabolic health. By managing your weight, you can stabilize insulin levels and protect your body from chronic diseases.
Reduced Inflammation and Cancer Risk
Decreased Chronic Disease Risk
Excess body fat contributes to chronic inflammation, which damages cells and increases cancer risk. Weight loss reduces the production of inflammatory cytokines, protecting your DNA from harm. Bariatric surgery patients, for example, experience a significant reduction in inflammation and a lower risk of hormonally driven cancers. This highlights the importance of weight loss in preventing chronic diseases and promoting long-term health.
Enhanced Immune Function
Carrying extra weight can weaken your immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off diseases, including cancer. Losing weight enhances immune function by reducing inflammation and improving hormone balance. A healthier immune system strengthens your body’s defenses, helping you stay resilient against cancer and other illnesses.
Overall Health and Longevity
Improved Quality of Life
Weight loss not only reduces cancer risk but also improves your overall quality of life. You may notice better mobility, increased energy, and a more positive outlook. Studies show that individuals who lose weight through bariatric surgery report significant improvements in their daily lives. These changes empower you to live a healthier, more fulfilling life.
Reduced Risk of Other Obesity-Related Conditions
Weight loss lowers the risk of other obesity-related conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, and kidney disease. Research indicates that patients who lose weight have a reduced risk of developing obesity-related cancers over three and five years. By prioritizing weight management, you can protect yourself from a wide range of health issues and enjoy a longer, healthier life.
💡 Tip: Small, consistent changes in your diet and activity levels can lead to lasting weight loss and significant health benefits.
Managing your weight is one of the most impactful steps you can take to reduce your cancer risk and improve your overall health. With nearly 2 billion adults worldwide living with overweight or obesity, the importance of maintaining a healthy weight cannot be overstated. Even small, sustainable changes in your daily habits—like eating more plant-based foods or staying active—can lead to significant health benefits. Avoiding excess body fat not only lowers your cancer risk but also enhances your quality of life. For personalized guidance, consult a healthcare professional and take charge of your health today.
FAQ
How does weight loss reduce cancer risk?
Losing weight lowers inflammation and stabilizes hormones like estrogen and insulin. These changes create a healthier environment in your body, reducing the chances of abnormal cell growth that leads to cancer. Even small weight loss can make a big difference.
Can exercise alone help prevent cancer?
Exercise plays a key role in cancer prevention. It helps you manage weight, reduce inflammation, and improve hormone balance. Pairing physical activity with healthy eating amplifies the benefits, giving you a stronger defense against cancer.
What foods should you avoid to lower cancer risk?
Avoid processed and fried foods. These often contain unhealthy fats and additives that promote weight gain and inflammation. Instead, choose whole, nutrient-rich options like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to support your health.
Is bariatric surgery a safe option for cancer prevention?
Bariatric surgery is safe for many people with severe obesity. It reduces cancer risk by helping you lose weight and improve hormone balance. Consult a specialist to see if this option fits your health goals.
How quickly can weight loss impact cancer risk?
Weight loss impacts cancer risk almost immediately. Hormone levels and inflammation begin to improve within weeks. Over time, consistent weight management leads to lasting health benefits and lower cancer risk.
💡 Tip: Start small. Every step toward a healthier weight brings you closer to reducing your cancer risk.
See Also
Recognizing Duodenal Cancer: Key Symptoms and Treatment Options
An In-Depth Overview of Various Cancer Types Available
Understanding Carcinoid Tumors: Essential Information You Need

